What Is Microfinance?
Microfinance refers to a variety of financial services, including loans, savings, insurance, and fund transfers, provided to individuals or small businesses that typically lack access to conventional banking services. The primary goal of microfinance is to empower low-income individuals by giving them the means to become self-sufficient through entrepreneurship. In many developing countries, microfinance institutions (MFIs) serve as a critical bridge, providing the financial support needed to foster economic growth and reduce poverty.
Encompassing several financial products and services tailored to meet the needs of the underserved, microfinance plays a crucial role.
- Microloans: Small loans provided to entrepreneurs to start or expand small businesses.
- Micro-savings: Savings accounts that cater to low-income individuals, offering them a safe place to save money.
- Micro-insurance: Insurance products designed to help low-income individuals manage risks such as health emergencies or natural disasters.
- Remittances and Payment Services: Financial services that facilitate the transfer of funds, especially for migrant workers sending money back home.
Importance of Understanding Microfinance

Understanding Microfinance in Sri Lanka is crucial for several reasons:
1. Poverty Alleviation:
In poverty reduction microfinance plays a essential role by providing financial services to those excluded from traditional banking. By enabling entrepreneurship and self-employment, microfinance helps individuals and families increase their income and improve their standard of living.
2. Economic Development:
Contributing to economic development by fostering a culture of entrepreneurship, microfinance supports small businesses financed through microloans to create jobs, stimulate economic activity, and contribute to community development.
3. Financial Inclusion:
One of the main goals of microfinance is to promote financial inclusion, ensuring that everyone has access to financial services. This inclusion is essential for economic stability and growth, as it allows more people to participate in the economy.
4. Women’s Empowerment:
Often targeting women, microfinance provides them with the financial means to start and grow their businesses, leading to greater gender equality and positive impacts on families and communities.
Key Principles of Microfinance
There are several microfinance principles that distinguish it from traditional banking:
• Diverse Financial Services for the Poor
Offering loans to low-income individuals is just on of the mere benefits of microfinance. It encompasses a wide range of financial services, including savings accounts, insurance products, and cash transfers. These services need to be flexible, convenient, and affordable to meet the varying needs of the poor. Particularly, micro-savings accounts enable the poor to save small amounts regularly, providing them with a safety net for future needs or emergencies. Micro-insurance protects against unforeseen events, reducing vulnerability and promoting financial stability.
• Combating Poverty with Financial Tools
Comparatively microfinance is a potent tool in the fight against poverty. By providing access to financial services, microfinance empowers the poor to increase their incomes, build assets, and reduce their susceptibility to external shocks. Additionally, access to credit allows poor households to move beyond mere survival, enabling them to invest in better nutrition, improved living conditions, and their children’s education and health. This financial empowerment leads to a more stable and prosperous future for low-income families.
• Establishing Inclusive Financial Systems
In many developing countries, a significant portion of the population lacks access to basic financial services. Microfinance aims to build financial systems that serve these underserved populations. Rather than being viewed solely as a development concern, microfinance should be integrated into the broader financial sector to reach its full potential. By doing so, it can provide sustainable financial services to a larger number of poor individuals and contribute to overall economic development.
• Financial Sustainability for Broad Reach
For microfinance institutions (MFIs) to reach significant numbers of poor people, they must achieve financial sustainability. This involves covering all operational costs, reducing transaction costs, and offering products that meet clients’ needs. Furthermore, financially sustainable MFIs can operate independently of donor funds, allowing them to scale their services and have a broader impact. Sustainability ensures the ongoing provision of financial services to the poor, fostering long-term economic development.
• Building Permanent Local Financial Institutions
Creating robust, local financial institutions is crucial for delivering long-term financial services to the poor. These institutions should be capable of mobilizing and recycling domestic savings, extending credit, and providing a range of financial products. Because of microfinance over time dependence on donor and government funding should decrease as these local institutions and private capital markets mature, leading to a more sustainable and self-sufficient microfinance sector.
• Tailoring Financial Solutions
Since microcredit is not a one-size-fits-all solution, It may not be suitable for everyone. Particularly the extremely poor who lack the means to repay loans. For such instances, other forms of support, like small grants, infrastructure improvements, employment programs, and non-financial services, may be more appropriate. These supports should ideally be coupled with savings programs to provide a comprehensive approach to poverty alleviation.
• Sensible Interest Rate Policies
Generally interest rate ceilings can hinder the ability of microfinance institutions to cover their costs and sustain their operations. As a result it is more costly to issue many small loans than a few large ones. Therefore, microlenders need to charge interest rates that reflect their operational costs. However, these rates should be kept reasonable to avoid exploiting borrowers. Governments should avoid setting interest rate caps that are too low and focus on creating a supportive policy environment for sustainable microfinance.
• Government as an Enabler
Governments play a critical role in fostering a supportive environment for microfinance. Because of which they should focus on maintaining macroeconomic stability, avoiding interest-rate caps, and refraining from market distortions through unsustainable loan programs. Governments can also enhance financial inclusion by improving the business environment, reducing corruption, and improving access to infrastructure and markets. In special cases, government funding may be necessary to support sound and independent microfinance institutions.
• Complementing Private Sector Capital with Donor Subsidies
Donor subsidies should be used strategically to complement private sector capital, not compete with it. These subsidies can build the institutional capacity of financial providers, develop supporting infrastructure, and support innovative services and products. Further in areas that are hard to reach, long-term donor support may be necessary. As a result effective donor funding should integrate financial services for the poor into local markets, apply specialist expertise, and set performance standards for continued support.
• Building Capacity
The lack of institutional and human capacity is a significant constraint in the microfinance sector. Considering building capacity is essential at all levels, from financial institutions to regulatory bodies and donor agencies. Investments should focus on developing the necessary skills and infrastructure to support a comprehensive and sustainable microfinance sector.
• Ensuring Transparency
Transparency in financial and social performance is crucial for the credibility and effectiveness of microfinance institutions. Accurate and comparable information allows clients, regulators, donors, and investors to assess risks and returns adequately. Likewise, transparency helps build trust among all stakeholders and ensures that financial services are delivered effectively and responsibly.
Pros and Cons of Microfinance in Sri Lanka
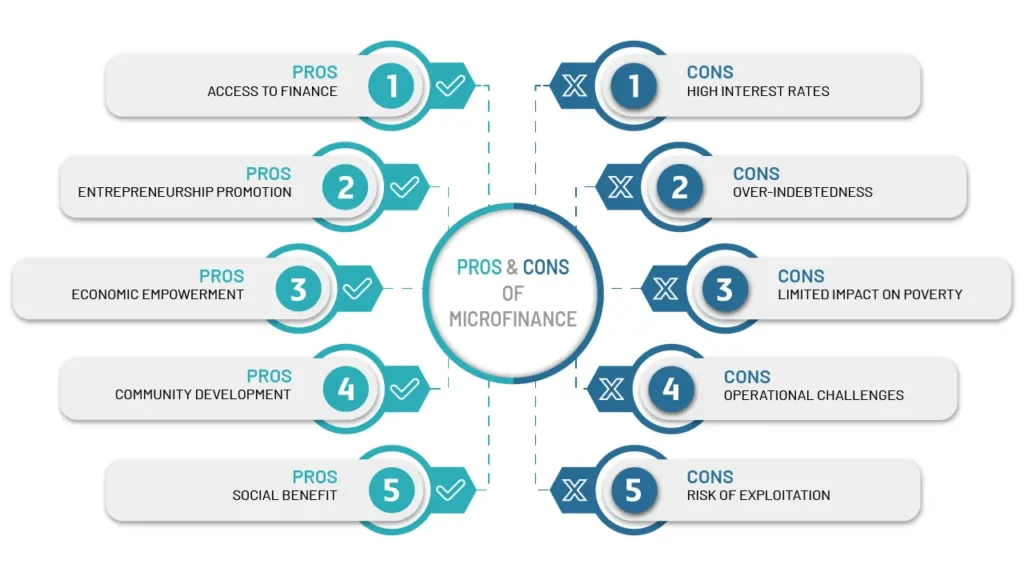
Pros:
Access to Finance: Microfinance provides financial access to those who are traditionally excluded from the formal banking sector.
Entrepreneurship Promotion: By providing the necessary capital, microfinance encourages entrepreneurship and self-employment.
Economic Empowerment: Microfinance empowers individuals, particularly women, by giving them control over their financial resources.
Community Development: Successful microenterprises contribute to the development of their communities through job creation and economic activities.
Social Benefits: Access to financial services can lead to improved health, education, and overall quality of life.
Cons:
High Interest Rates: Some microfinance institutions charge high interest rates to cover their operational costs, which can be burdensome for borrowers.
Over-Indebtedness: Without proper financial education, some borrowers may take on more debt than they can handle, leading to financial stress.
Limited Impact on Poverty: While microfinance can improve income levels, it may not always lead to significant reductions in poverty or address deeper systemic issues.
Operational Challenges: Microfinance institutions often face challenges related to sustainability, efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Risk of Exploitation: In some cases, the focus on financial sustainability can lead to practices that exploit borrowers, such as aggressive loan recovery methods.
FirstMicro is an innovative financial software designed to revolutionize microfinance operations in Sri Lanka. This comprehensive solution is tailored to meet the unique needs of microfinance institutions, enhancing their efficiency, scalability, and impact.
Key Modules of FirstMicro
- Efficient Customer Management: FirstMicro provides robust client management tools, allowing MFIs to track client information, loan histories, and repayment schedules efficiently. This module ensures a seamless customer experience, enabling staff to manage and serve clients effectively.
- Streamlined Loan Management: The software automates the loan application, approval, and disbursement processes, ensuring timely and accurate loan management. It includes features for risk assessment and loan performance tracking, making loan management hassle-free.
- Group Lending Reports & Enquiries: FirstMicro offers over 20 system-generated reports tailored for group lending. These reports provide detailed insights into group loan performance, member activities, and repayment schedules, helping MFIs make informed decisions.
- Improved Loan Follow-up Processes: The software enhances loan follow-up processes with features designed to monitor repayments and manage delinquencies effectively. This ensures that MFIs can maintain high repayment rates and minimize defaults.
- Automated Alerts & Notifications: FirstMicro includes automated alerts and notifications to keep both clients and staff informed about notable events, such as upcoming repayments, overdue payments, and loan approvals. This feature helps in maintaining clear communication and reducing missed payments.
- Comprehensive Payment Management: The payment management module supports various payment methods, enabling clients to repay loans conveniently. It also includes reconciliation features to ensure accurate financial records.
- Field Agent Mobile App (Available upon request): Recognizing the importance of mobile technology in expanding financial inclusion, FirstMicro offers a mobile app for field agents. This app allows agents to manage client interactions, collect payments, and update loan information in real-time, improving field operations.
- Automated General Ledger: The software includes an automated general ledger that streamlines financial accounting processes. This module ensures accurate financial reporting and compliance with regulatory requirements, reducing the administrative burden on MFIs.
Benefits of FirstMicro for Microfinance Institutions in Sri Lanka
• Improved Efficiency: By automating key processes, FirstMicro helps MFIs reduce operational costs and improve service delivery, allowing them to reach more clients effectively.
• Enhanced Client Experience: The software’s user-friendly interface and mobile integration enhance the client experience, making it easier for clients to access financial services and manage their accounts.
• Scalability: FirstMicro supports the growth and scalability of MFIs by providing the tools needed to manage a larger client base and expand their services.
• Data-Driven Decision Making: With comprehensive reporting and analytics, FirstMicro enables MFIs to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and better serve their clients.
• Financial Inclusion: By leveraging technology, FirstMicro helps MFIs extend their reach to underserved communities, promoting financial inclusion and economic development in Sri Lanka.
Conclusion
Microfinance plays a crucial role in empowering individuals and fostering economic development, particularly in developing countries like Sri Lanka. Understanding its principles, benefits, and challenges is essential for realizing its full potential. With innovative solutions like FirstMicro, microfinance institutions can enhance their operations, reach more clients, and drive meaningful change. By embracing technology and focusing on client needs, FirstMicro is set to revolutionize microfinance in Sri Lanka, paving the way for a more inclusive and prosperous future.



