Financial technology, or FinTech, refers to the innovative use of technology to provide financial services. It encompasses a wide range of applications, from mobile banking and payment solutions to blockchain and artificial intelligence-driven financial products. FinTech is transforming the financial landscape globally by making financial services more accessible, efficient, and secure. In Sri Lanka, the adoption of FinTech is accelerating, driven by mobile innovation and a growing demand for digital financial solutions.
1. The Rise of Financial Technology in Sri Lanka
FinTech has rapidly gained momentum in Sri Lanka over the past decade. The adoption of mobile technology, increasing internet penetration, and a growing demand for digital financial services have all contributed to this rise. As traditional banking methods evolve, FinTech solutions are offering more efficient, secure, and accessible alternatives to the Sri Lankan population.
1.1. Key Drivers
Several factors are driving the growth of financial technology in Sri Lanka:
• Mobile Penetration: With a sizable portion of the population owning smartphones, mobile banking and payment solutions have become more accessible.
• Government Initiatives: The Sri Lankan government has introduced policies and regulations to promote digital payments and financial inclusion.
• Consumer Demand: There is a growing demand for convenient, fast, and secure financial services that traditional banks are sometimes slow to provide.
• Investment and Innovation: Increased investment in the FinTech sector and a focus on innovation are leading to the development of innovative financial solutions.
2. FinTech Solutions Transforming Sri Lanka
FinTech solutions in Sri Lanka have been introducing new ways to handle financial transactions and manage money. Some of the most impactful solutions include:
Mobile Payments: Apps like EzCash and Genie have made it easier for people to send and receive money, pay bills, and make purchases using their mobile phones.
Digital Banking: Banks are now offering digital services that allow customers to open accounts, apply for loans, and manage their finances online without visiting a branch.
Peer-to-Peer Lending: Platforms that facilitate lending between individuals are providing an alternative to traditional bank loans, often with lower interest rates.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: Although still in the initial stages, blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies are starting to gain traction in Sri Lanka, offering secure and transparent financial transactions.
3. Types of FinTech Users
FinTech solutions have a wide range of users, each with unique needs and preferences. Understanding these user types can help tailor financial technology solutions more effectively:
1. Consumers: Individuals using FinTech for personal finance management, mobile payments, budgeting, and investing. They seek convenience, security, and personalized services.
2. Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs): Businesses that use FinTech for payment processing, accounting, and financial management. They look for tools that streamline operations and improve financial efficiency.
3. Large Corporations: Large enterprises utilize advanced FinTech solutions for complex financial operations, risk management, and global transactions. They require scalable and secure solutions that integrate with existing systems.
4. Financial Institutions: Banks, credit unions, and investment firms adopting FinTech for digital banking, customer engagement, and data analytics. They aim to enhance customer service and operational efficiency.
5. Developers and Innovators: Individuals and companies creating new FinTech applications and technologies. They need robust platforms, tools, and support to build and scale their solutions.
4. Finance Technology History & Landscape
4.1. Historical Overview
The history of financial technology dates back to the late 20th century when digital solutions began transforming traditional banking practices. Early innovations included the introduction of ATMs and electronic funds transfers, which significantly enhanced convenience and efficiency.
1980s – 1990s: The advent of online banking marked the beginning of digital financial services, allowing customers to access their accounts and conduct transactions via the internet.
2000s: The rise of mobile phones and smartphones introduced mobile banking and payment solutions, making financial services more accessible to a broader audience.
2010s: The emergence of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, along with the proliferation of FinTech startups, reshaped the financial landscape with new payment methods and financial instruments.
4.2. Current Landscape
Today, the FinTech landscape is characterized by rapid technological advancements and a growing number of innovative solutions:
• Digital Payments: Mobile wallets, peer-to-peer payment platforms, and contactless payments have become mainstream.
• Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: These technologies are driving new forms of digital assets and decentralized financial systems.
• Regulatory Technology (RegTech): Solutions that help financial institutions comply with regulations and manage risk more effectively.
• Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is used for fraud detection, customer service automation, and personalized financial advice.
Open Banking: Open banking is gaining traction as it allows third-party providers to access consumer banking data through APIs, promoting innovation and competition in financial services.
5. The Role of Open Banking in Fintech
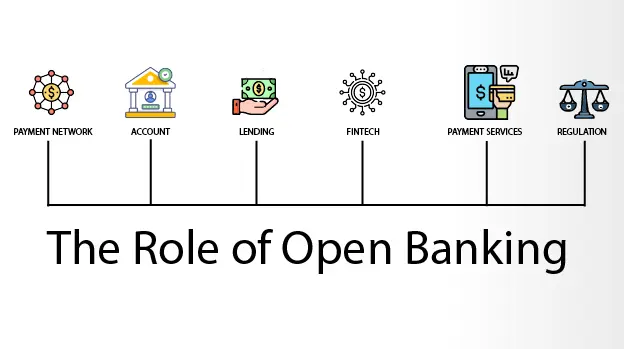
Open banking is a system that allows third-party financial service providers to access consumer banking information through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). This model is gaining popularity worldwide and holds significant promise for the future of financial technology in Sri Lanka.
5.1. Benefits of Open Banking
- Increased Competition: Open banking fosters competition among financial service providers, leading to better services and lower costs for consumers.
- Innovation: By enabling access to banking data, open banking encourages the development of new and innovative financial products and services.
- Improved Customer Experience: Customers can benefit from personalized financial services tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
- Financial Inclusion: Open banking can help bring more people into the formal financial system by providing easier access to financial services.
6. Challenges and Opportunities of Financial Technology
While the rise of financial technology presents numerous opportunities, it also comes with challenges that need to be addressed:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating the complex landscape of local and international regulations can be a significant barrier. Ensuring compliance with financial regulations and standards requires constant adaptation and investment in legal expertise.
- Consumer Trust and Adoption: Convincing consumers to transition from traditional financial methods to new FinTech solutions can be challenging. Building trust through security, reliability, and transparent practices is crucial for widespread adoption.
- Infrastructure Development: Developing the necessary infrastructure to support widespread FinTech adoption, particularly in underserved and rural areas, remains a challenge. This includes investing in reliable internet access and digital literacy programs.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many financial institutions struggle with integrating new FinTech solutions with existing legacy systems. This can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs. Seamless integration is essential for achieving the full benefits of FinTech innovations.
- Market Competition: The rapid pace of innovation in FinTech leads to intense competition among startups and established players. Staying ahead requires continuous investment in technology and understanding evolving market needs.
- Scalability: Ensuring that FinTech solutions can scale effectively to accommodate growing user bases and expanding services is a critical challenge. Solutions must be designed with scalability in mind to manage increased demand and complexity.
7. The Future of Banking in Sri Lanka
The future of banking in Sri Lanka looks promising, with financial technology playing a leading role. As FinTech solutions continue to evolve, we can expect:
• Greater Financial Inclusion: More people will have access to financial services, helping to reduce poverty and improve economic stability.
• Enhanced User Experience: FinTech innovations will provide more convenient, efficient, and personalized financial services.
• Increased Collaboration: Traditional banks and FinTech companies will collaborate more closely to offer comprehensive financial solutions.
• Continued Innovation: The FinTech sector will keep evolving, bringing recent technologies and solutions that address the unique needs of the Sri Lankan market.
8. Technologies Shaping the Future of FinTech in Sri Lanka
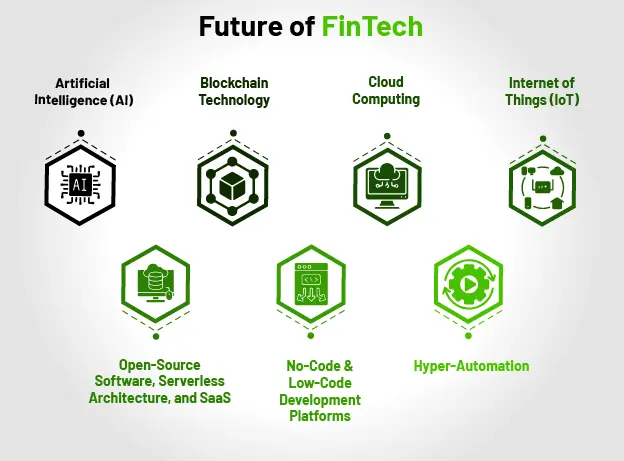
Several innovative technologies are set to shape the future of FinTech in Sri Lanka, driving growth in this competitive landscape:
• Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is set to revolutionize the financial sector by automating complex tasks and providing deeper insights into customer behavior. AI-powered tools can enhance decision-making, detect fraud more effectively, and personalize financial services. The potential value created by AI technologies is immense, with projections suggesting a contribution of up to $4.4 trillion annually to the global economy.
• Blockchain Technology
Blockchain offers a decentralized way to record transactions securely, which can disrupt traditional financial systems. By storing data across multiple locations, blockchain enhances transparency and security. Key innovations such as smart contracts, which automate agreements, and distributed ledgers are driving advancements in digital wallets, cryptocurrencies, and decentralized finance.
• Cloud Computing
Cloud technology is transforming financial services by providing scalable and cost-effective solutions. By 2030, cloud computing is expected to significantly reduce operational costs and boost efficiency for financial institutions. Its flexibility allows FinTech companies to quickly adapt to changing market demands and scale their services with ease.
• Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT integrates connected devices and sensors to collect and analyze data in real-time. In finance, this technology supports enhanced customer service through smart sensors and improves operational efficiency with advanced data analytics. IoT applications can provide valuable insights and streamline various financial processes.
• Open-Source Software, Serverless Architecture, and SaaS
These technologies are critical for modern FinTech development. Open-source software and serverless architecture offer flexibility and scalability, while Software as a Service (SaaS) provides on-demand solutions without the need for extensive infrastructure. Together, they enable faster deployment of innovative financial services and help companies stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
• No-Code and Low-Code Development Platforms
No-code and low-code platforms allow users to create applications with minimal programming knowledge. These tools use graphical interfaces and pre-built components, making it easier and faster to develop and deploy FinTech solutions. This democratization of development accelerates innovation and enables more players to contribute to the FinTech ecosystem.
• Hyper-Automation
Hyper-automation combines AI, machine learning, and advanced analytics to automate complex processes and improve efficiency. By streamlining operations and enhancing decision-making, hyper-automation plays a crucial role in the future of FinTech. It helps financial institutions reduce manual effort, minimize errors, and deliver faster, more accurate services.

FinTech innovation in Sri Lanka includes MULA, a field agent mobile application developed by FINAP. MULA’s platform integrates seamlessly with both FirstMicro and ECOru, enhancing the capabilities of field agents and providing superior user experience.
MULA allows field agents to perform critical banking functions on-the-go, accelerating service delivery and improving customer interactions. Designed with the unique demands of the Sri Lankan market in mind, MULA not only boosts operational efficiency but also fosters a more connected and financially empowered society.
Through its software solutions, FINAP is enhancing Sri Lanka’s financial infrastructure and ensuring that every citizen can participate actively in the economy. As we look to the future, FINAP stands as a pillar of technological excellence and economic empowerment.
In conclusion, the rise of financial technology in Sri Lanka, driven by mobile innovation, is transforming the country’s financial landscape. With the continued development of FinTech solutions, the adoption of open banking, and the overcoming of existing challenges, Sri Lanka is well on its way to a more inclusive, efficient, and innovative financial future.